Tamarix gallica
Kingdom : Plantae / النّباتات
Division : Spermaphyta / البذريات
Clade : Magnoliophyta or Angiospermae / مستورات البذور
Class : Eudicotyledoneae / ذات الفلقتين
Order : Caryophyllales / رتبة القرنفليات
Family : Tamaricaceae / فصيلة الطرفائيات
Genus : Tamarix
species : gallica
Chromosomes: 2n=24
Protologue
L., Sp. Pl., ed. 1, 270 (1753)
Synonyms
Tamarix indica Willd. 33 = gallica Linn. Tamarix anglica Webb, Hook. J. Bot. 3: 430 (1841).
Common names
Tunisia Arabic English French Tamazight
الطرفة
الأثل
الطحطاح
الأَثل الفرنسي
البُجْمُ
French tamarisk
Tamaris commun
Tamaris de France
Tamarix
Tammemayt
Toxic
no
Edible
yes
Latex
no
Botanic description
Genus description
"
Species description
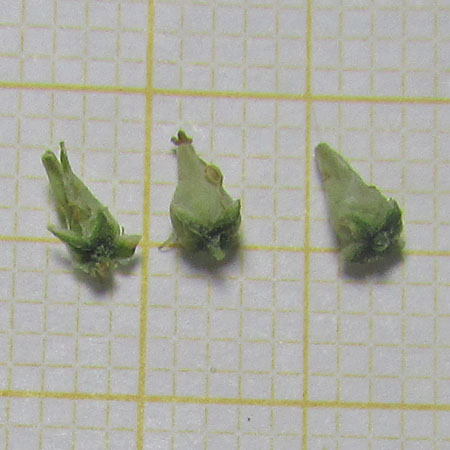
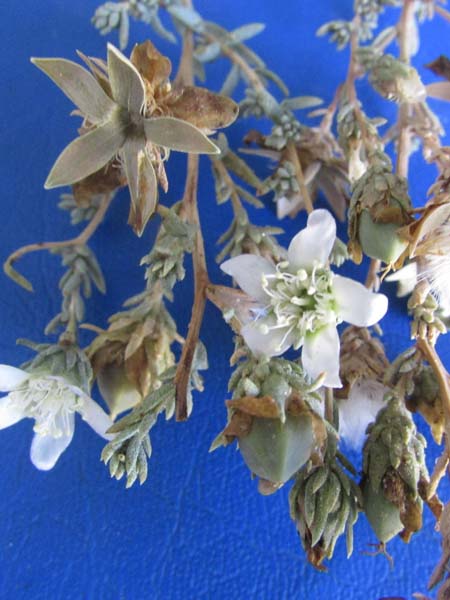
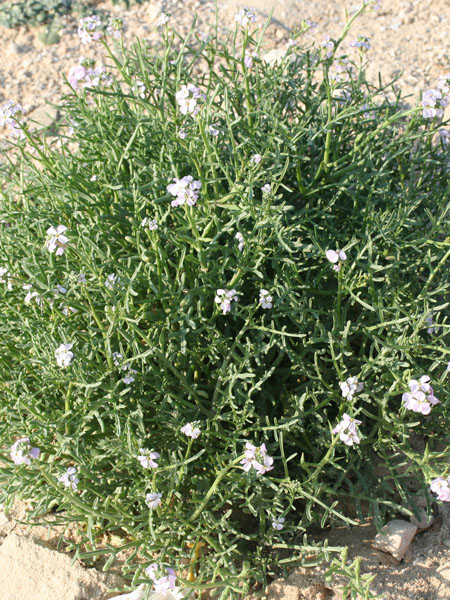
"Shrub or shrub with a feathery, feather-like appearance, 5 meters high, glabrous with bark brown to dark purple and with slender, tapered, reddish twigs. When he is not bloomed, it has a vague resemblance to certain conifers, resistant to diseases and parasites
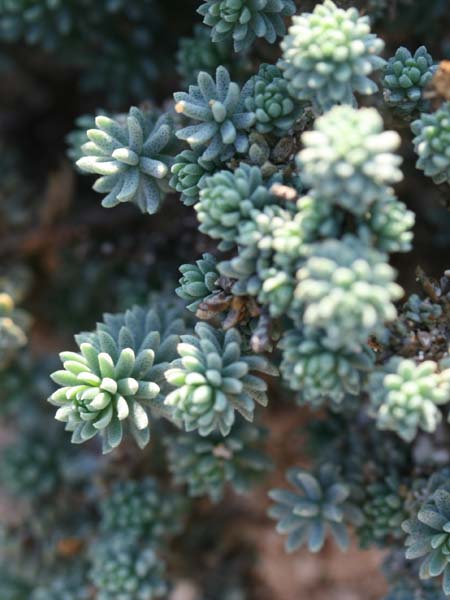
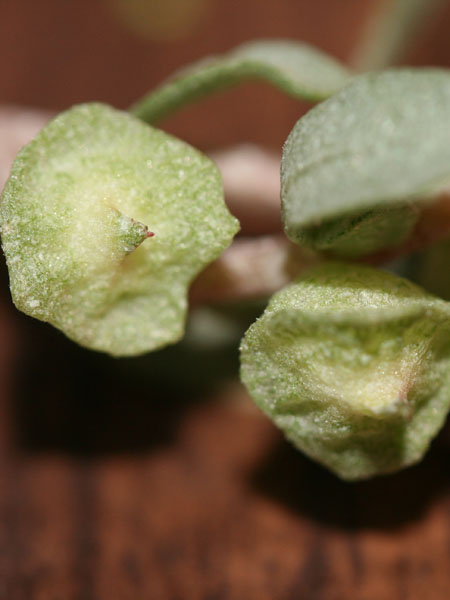
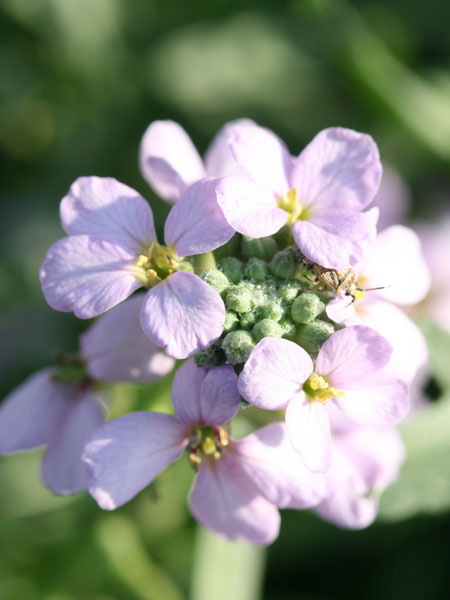
Stems slender, tapered, reddish. Leaves scales, bluish green to dark, oval to triangular, 0.1 - 0.4 cm, with half-stem base, acuminate, hugging, fleshy, opaque, white developing before the flowers. Flowers in compact clusters, pink, tinny, 2-3 mm wide more or less loose. The petals fall quickly but the 5 stamens stay a long time. Inflorescence raceme 3-5 mm wide only. Fruits Capsule, oval-pyramidal, containing many seeds. Insensibly attenuated from the base to the summit.
Botanic References
Pottier-Alapetite G. (1981). Flore de la Tunisie Angiospermes –Dicotylédones (Apétales- Dialypétale , Première partie). Imprimerie Officielle de la République Tunisienne (Eds), 516-517p. Edouard LE FLOC’H, Loutfy BOULOS et Errol VELA. (2010). Catalogue synonymique commenté de la FLORE DE TUNISIE. République Tunisienne, Ministère de l’Environnement et du développement durable, Banque Nationale de Gènes. 500 p www.theplantlist.org
Biology
Life form Perennial Type form Phanerophyte Photosynthesis C3
Phenology
Blooming
JanuaryFebruaryMarchAprilMayJuneJulyAugustSeptemberOctoberNovemberDecember
Fruiting
JanuaryFebruaryMarchAprilMayJuneJulyAugustSeptemberOctoberNovemberDecember
Map Localization
Ecology
Adaptation It resists very well to salt, and grows so very well along the coast. However, we can find at the edge of some rivers in the hinterland. The flowers are pinkish and appear simultaneously to leaves. It is a tree that is often planted at the seaside, but it is slightly sensitive to frost. Salt bladder yes Invasive no
Geographical distribution
Localization Biocimatic stage Annuel pluviometry (mm) GPS Monastir (Skanès, Juillet 2015) Inferior semi-arid 331 35°46'42.73"N / 10°47'38.99"E Monastir (Sidi Ghedemssi Nov.2014;) Inferior semi-arid 331 35°47'4.66"N / 10°49'58.28"E Sousse (Hergla, Déc 2013; 2016) Inferior semi-arid 331 36° 1'14.35"N / 10°25'35.09"E Bizerte (Ichkeul, Nov.2014) Lower humid - sub-humid 653 37° 7'2.10"N / 9°40'20.52"E
General uses
Windbreak hedge, free hedge.
Medicinal uses
"The bark and leaves of the tamarisk can be used for astringent, sudorific, aperitive and diuretic, expectorant and laxative action. The flowers are applied as a poultice to skin abscesses, wounds and firm furuncle to heal them. The galls are prescribed in the form of an infusion or decoction for their anti-inflammatory, healing, antiseptic, astringent, anti-diarrheal, diuretic, expectorant and laxative properties. They are also used for tanning leathers and for dyeing the hair. Currently, all species of tamarisk (leaves, flowers, and galls) are widely used in the traditional Asian pharmacopoeia. The extracts of this plant are also used against disorders of the spleen and ocular diseases. The methanol extract has been studied for its chemo-protective and anti-carcinogenic activities by evaluating the level of hepatic antioxidant defense. A recent study has shown its antibacterial activity.
NOTE : This website is not that of herbal medicine and assumes no responsibility for the negative effects of the use of plants. Seek advice from a professional before using a medicinal plant.
Systems / Organs / Effects
Digestive System Urinary System Respiratory System Eays Diaphoretic Antiseptic Antiinflammatory Astringent Skin
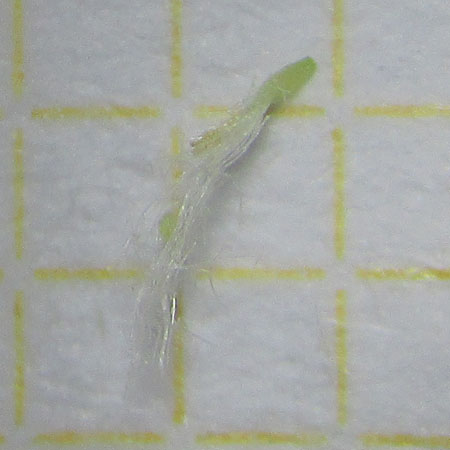
Description of the seeds
Form linear External structure pappus Ornamentation Type of seed Average length of 10 seeds 2.3 ± 0,1 (mm) Average width of 10 seeds 0.1 ± 0.01 (mm) Average thickness of 10 seeds 0.1 ± 0.01 (mm) Average mass of 100 seeds 0.6 (g)
Test results
TPC DPPH ABTS+ FRAP Year mg GAE g-1 MS CI50 g ml-1 CI50 g ml-1 CE50 g ml-1 89,00± 1,32 17,17± 1,18 26,55± 0,47 167,35± 2,32 2016 Total Phenols content(TPC), Anti-radical potentialities against (DPPH, ABTS), Ferric reducing antioxidant power(FRAP)
Molecules : ADN / Proteins
Chromosomes : 24 Uniprot NCBI
Tunisian references
Boulaabaa M, Snoussi M, Saada M, Mkadmini K, Smaoui A, Abdelly C, Ksouri R (2015). Antimicrobial activities and phytochemical analysis of Tamarix gallica extracts. Industrial Crops and Products.76, 1114–1122. Chaieb M et Boukhris M (1998). Flore succincte et illustrée des zones arides et sahariennes de Tunisie. Association pour la protection de la nature et de l’environnement, Sfax. 209 p. Ksouri R, Falleh H, Megdiche, W., Trabelsi, N., Mhamdi, B., Chaieb, K., Bakrouf, A, Magne C, Abdelly C, (2009). Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of the edible medicinal halophyte Tamarix gallica L. and related polyphenolic constituents. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 2009; 47 (8), 2083–2091. Saidana D, Mahjoub MA, Boussaada O, Chriaa J, Cheraif I, Daamid M, Mighrib Z, Helal AN (2008). Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of volatile compounds of Tamarix boveana (Tamaricaceae). Microbiol Res; 163, 445–455.20.
-
Other references
Chaturvedi S, Drabu S, Sharma M.(2012). Anti- inflammatory and analgesic activity of Tamarix gallica Int J Pharm Pharm Sci. Vol 4, Suppl 3, 653-658.