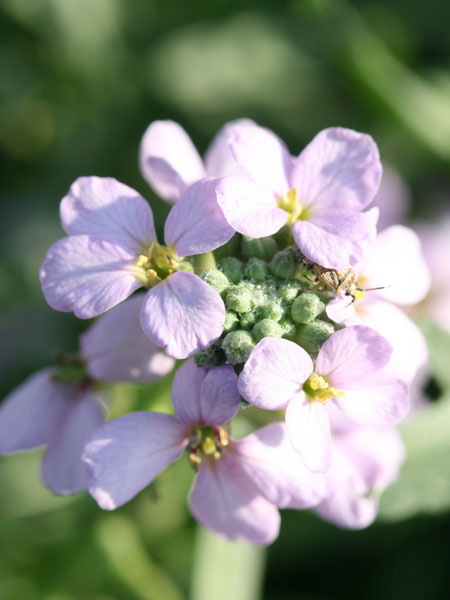
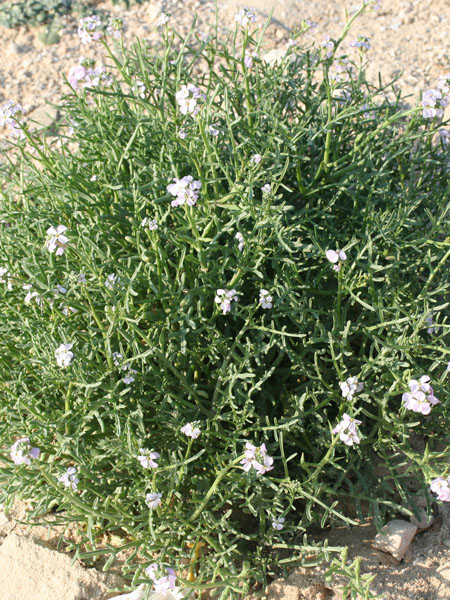
Carpobrotus edulis
Kingdom : Plantae / النّباتات
Division : Spermaphyta / البذريات
Clade : Magnoliophyta or Angiospermae / مستورات البذور
Class : Eudicotyledoneae / ذات الفلقتين
Order : Caryophyllales / رتبة القرنفليات
Family : Aizoaceae /الفصيلة المليحيّة
Genus : Carpobrotus
species : edulis
Chromosomes: 2n=18
Protologue
(L.) N.E. Br. in E.P. Phillips, Gen. S. Afr. Fl. Pl. 249 (1926)
Synonyms
Abryanthemum edule (L.) Rothm., 1941. Mesembryanthemum edule L., Syst. Nat., ed. 10, 1060 (1759).
Common names
Tunisia Arabic English French Tamazight
شرببّو
اصبع زينب (Algérie)
اصابع العروس (Syrie)
Elands Sourfig
Elands suurvy
Sally-my-handsome
Red Hottentot-fig
Hottentot FigCroc de sorcière Griffe de sorcière Doigt de fée Ficoïde comestible Figuier des Hottentots Doigt de sorcière
Toxic
no
Edible
yes
Latex
no
Botanic description
Genus description
"Flowers with calyx formed of 5 sepals, welded at the base between them and with the ovary. Many linear petaloid staminodes. Many etamines inserted in several rows. Carpels 5-12. Capsule at 5 angles, umbilicated first fleshy, then becoming woody and opening in star. Succulents.
Species description
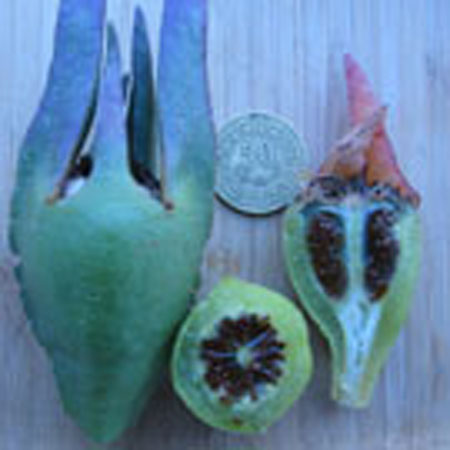
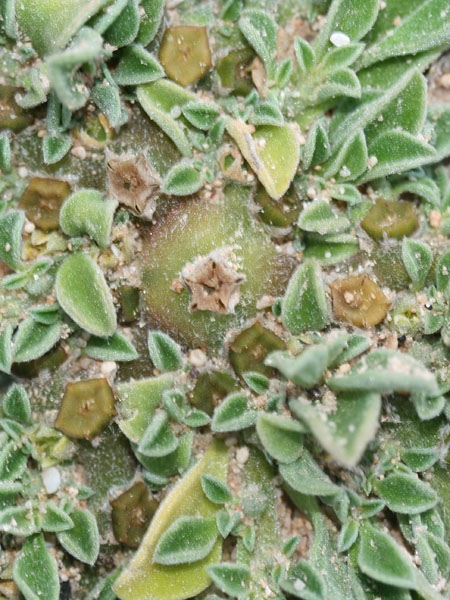
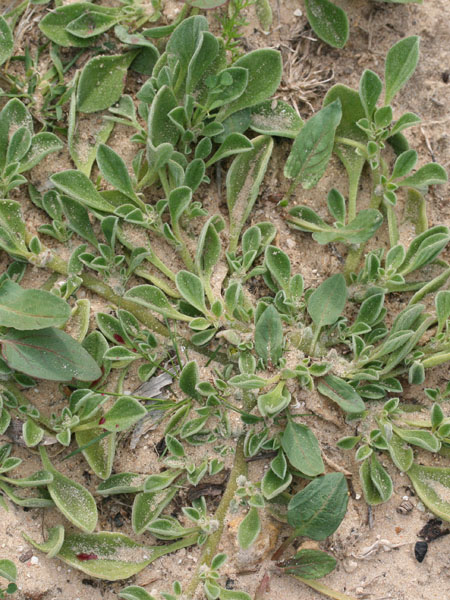
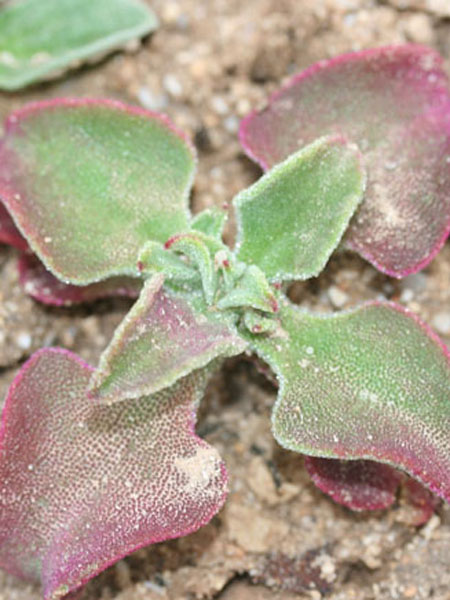
"Invasive sub-shrub, robust, creeping, succulent, evergreen, lining, fast-growing, growing all year round (more than 1 m per year).
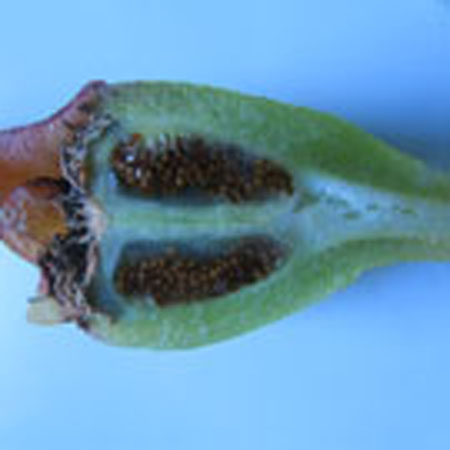
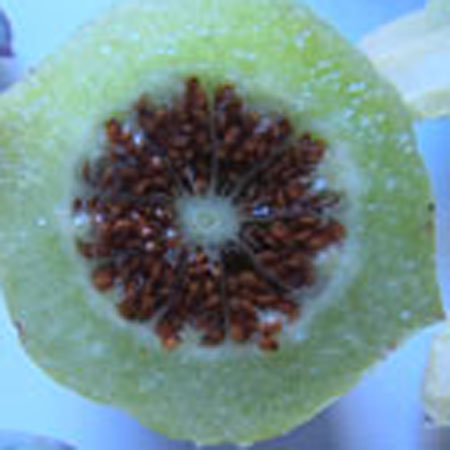
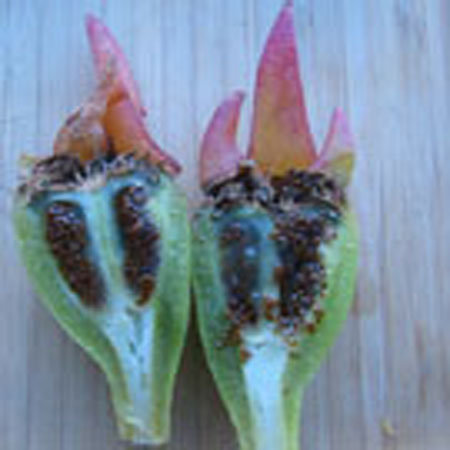
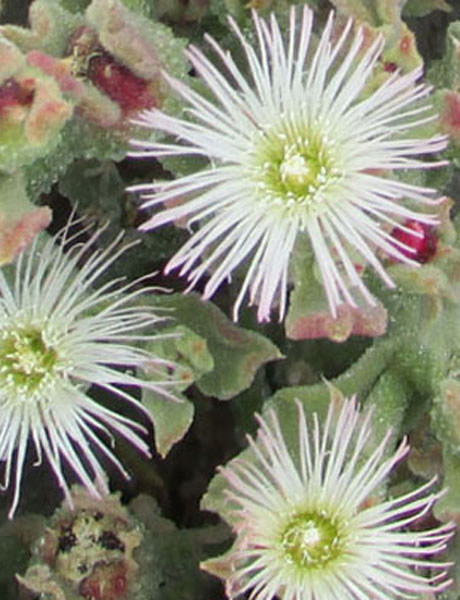
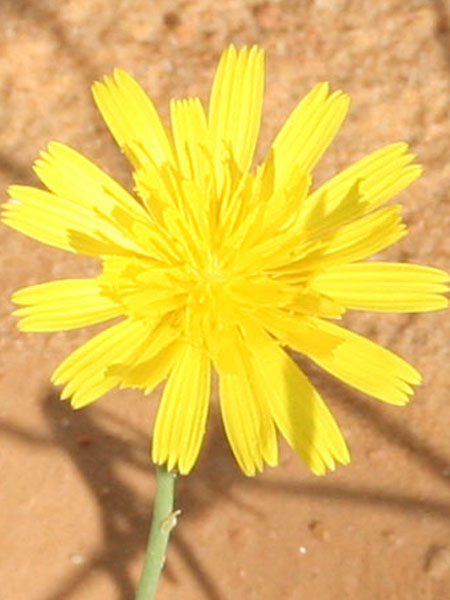
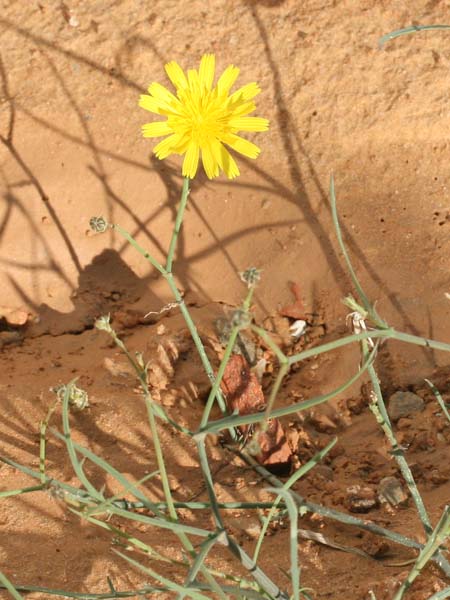
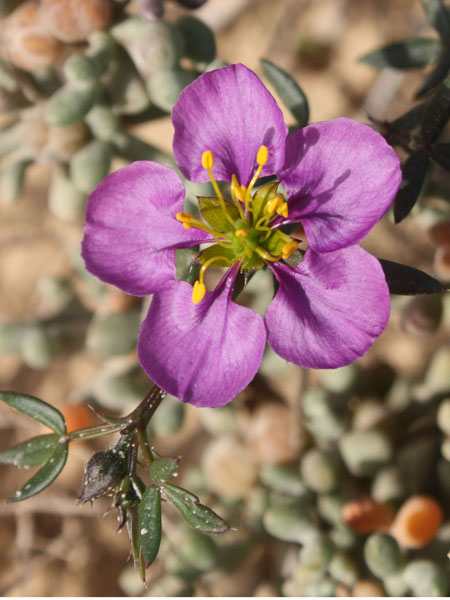
Stems lying more than 1 m with a diameter of 1 cm or more, flat bent, woody at the base, sometimes slightly reddish. Leaves triqueter, smooth, opposite, succulent, falciform trigonal and triangular sectional, welded and sheathing at the base, 8-12 cm long and about 1 cm wide hull scabrous towards the end. Flowers ornamental, very large, reaching largely 10 cm in diameter, yellow, orange, dark red, pink, purple, solitary. Stigmates 8-12, on a fleshy disc. Fruits Large conical capsule, welded to the tube of the perigonium, marked with 2 prominent ribs. Seeds many small and usually aborted in a mucilaginous fluid.
Botanic References
Pottier-Alapetite G. (1981). Flore de la Tunisie Angiospermes –Dicotylédones (Apétales- Dialypétale , Première partie). Imprimerie Officielle de la République Tunisienne (Eds),81 p. Edouard Le Floc’h, Loutfy Boulos et Errol Vela. (2010). Catalogue synonymique commenté de la Flore de Tunisie. République Tunisienne, Ministère de l’Environnement et du développement durable, Banque Nationale de Gènes. 500 p www.theplantlist.org
Biology
Life form perennial Type form Hemicryptophyte Photosynthesis C3,CAM
Phenology
Blooming
JanuaryFebruaryMarchAprilMayJuneJulyAugustSeptemberOctoberNovemberDecember
Fruiting
JanuaryFebruaryMarchAprilMayJuneJulyAugustSeptemberOctoberNovemberDecember
Map Localization
Ecology
Adaptation The plant grows easily on mesic soils, usually on marine sands. Salt bladder yes Invasive yes
Geographical distribution
Localization Biocimatic stage Annuel pluviometry (mm) GPS Djerba (Déc.2013) Higher arid 209 33°51'49 N / 10°47'37E Monastir (Déc.2013) Inferior semi-arid 331 35°46'42.41"N /10°47'37.19"E Cap Bon (Fév.2016, Tazerka) Superior semi-arid 444 36°32'21.62"N / 10°50'55.54"E Cap Bon (Menzel Temim, Fév.2016) Superior semi-arid 444 36°46'4.32"N / 11° 0'21.18"E Cap Bon (Fév.2016, Kélibia, Haouria) Superior semi-arid 444 36°50'2.98"N / 11° 7'0.73"E
General uses
Ornamental plant thanks to their beautiful flowers.
Medicinal uses
"It has anti-inflammatory healing properties placed as antiseptic dressing on wounds, burns, abrasions, cuts, scratches, sunburns and against inflammations caused by jellyfish. It is also used against ringworm, infantile eczema, dermatitis, herpes, lily of the valley, cold sores, chapped lips, skin allergies.
Remedy for bacterial and fungal infections in the treatment of sinusitis and tuberculosis. Old remedy against constipation (fruit with salt water).Leaf juice is a mild astringent, can be gargled to treat mild bacterial infections of the mouth and sore throat and diluted in water, can be used to treat diarrhea, dysentery and stomach cramps . The syrup made from the fruits has laxative properties.
NOTE : This website is not that of herbal medicine and assumes no responsibility for the negative effects of the use of plants. Seek advice from a professional before using a medicinal plant.
Systems / Organs / Effects
Respiratory System Mouth / Teeth Eays Antiseptic Antiinflammatory Skin
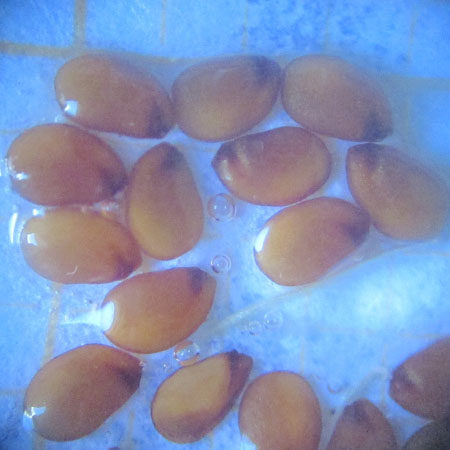
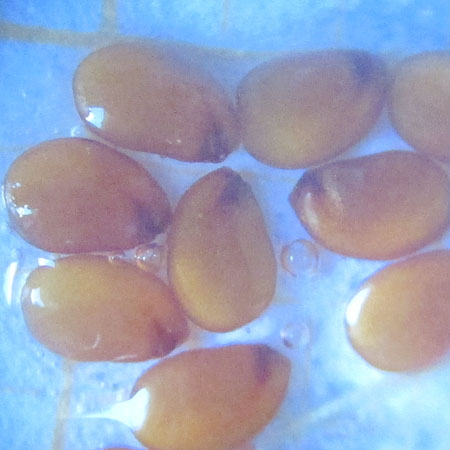
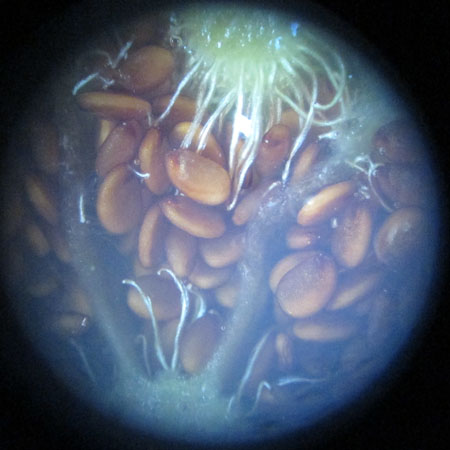
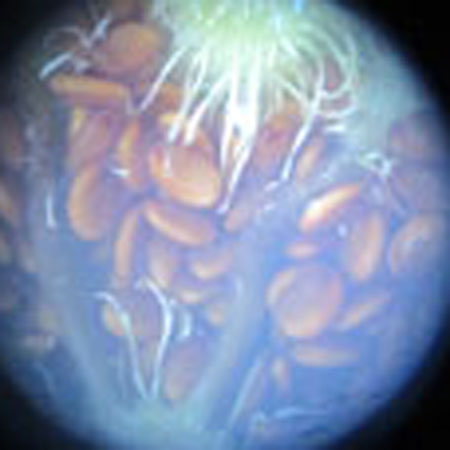
Description of the seeds
Form elliptic External structure any Ornamentation any Type of seed any Average length of 10 seeds 1.5 ± 0,1 (mm) Average width of 10 seeds 1 ± 0,1 (mm) Average thickness of 10 seeds 0.1 ± 0,01 (mm) Average mass of 100 seeds (g)
Test results
TPC DPPH ABTS+ FRAP Year mg GAE g-1 MS CI50 g ml-1 CI50 g ml-1 CE50 g ml-1 172,50 ± 3,04 32,30 ± 0,30 44,36± 0,14 89,00± 1,44 2016 Total Phenols content(TPC), Anti-radical potentialities against (DPPH, ABTS), Ferric reducing antioxidant power(FRAP)
Molecules : ADN / Proteins
Chromosomes : 18 Uniprot NCBI
Tunisian references
Bouftira I., Chedly A., Souad S. (2012). Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum and Carpobrotus edulis Extracts Advances in Chemical Engineering and Science, 2, 359-365. Boukef M.K. (1986). Les plantes dans la médécine traditionnelle tunisienne. Médécine traditionnelle et pharmacopée. Librairie La rose (Eds), Paris, 350p. Chaieb M., Boukhris M. (1998). Flore succincte et illustrée des zones arides et sahariennes de Tunisie. Association pour la protection de la nature et de l’environnement, Sfax. 184 p. Falleh H., Ksouri R., Medini F., Guyot S., Abdelly C., Magne C. (2011). Antioxidant activity and phenolic composition of the medicinal and edible halophyte Mesembryanthemum edule L. Ind Crops Prod, 34, 1066–1071. Falleh H., Ksouri R., Oueslati S., Guyot S., Magne C., Abdelly C. (2009). Interspecific variability of antioxidant activities and phenolic composition in Mesembryanthemum genus. Food Chem Toxicol, 47, 2308–2313. Falleh H., Oueslati S., Guyot S., Ben Dali A., Magné C., Abdelly C., Ksouri R. (2011a). LC/ESI-MS/MS characterisation of procyanidins and propelargonidins responsible for the strong antioxidant activity of the edible halophyte Mesembryanthemum edule L. Food Chem, 127, 1732–1738. Falleh H., Ksouri R., Lucchessi M.E., Abdelly C., Magné C.(2012). Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction: Effect of Extraction Time and Solvent Poweron the Levels of Polyphenols and Antioxidant Activity of Mesembryanthemum edule L. Aizoaceae Shoots Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research ; 11 (2): 243-249. Falleh H., Trabelsi N., Bonenfant-Magné M.,Le Floch G., Abdelly C., Magné C., Ksouri K.(2013). Polyphenol content and biological activities of Mesembryanthemum edule organs after fractionation Industrial Crops and Products 42 : 145– 152. 16.
Other references
Chinnock R.J. (1972). Natural hybrids between Disphyma and Carpobrotus (Aizoaceae) in New Zealand New Zealand Journal of Botany /0: 615-26. D'Antonio C.M. (1993). Mechanisms controlling invasion of coastal plant-communities by the alien succulent Carpobrotus edulis. Ecology 74: 83-95. Custódio L., Ferreira A.C., Pereira H., Silvestre L., Vizetto-Duarte C., Barreira L., Rauter P.A., Alberício F., Varela J. (2012). The marine halophytes Carpobrotus edulis L. and Arthrocnemum macrostachyum L. are potential sources of nutritionally important PUFAs and metabolites with antioxidant, metal chelating and anticholinesterase inhibitory activities Botanica Marina 55; 281–288. Van der Watt E. et Pretorius J.C. (2001). Purification and Identification of Active Antibacterial Components in Carpobrotus edulis L. Journal of Ethnopharmcology, Vol. 76, N°. 1, pp. 87-91.